Any other miswires
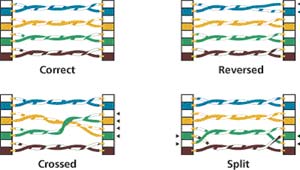
A reversed pair occurs when the polarity of one wire pair
is reversed at one end of the link (also called a tip/ring
reversal). A crossed (or transposed) pair occurs when the
two conductors in a wire pair are connected to the position
for a different pair at the remote connector. Split pairs
occur when pin to pin continuity is maintained but physical
pairs are separated. Refer to the figure below for an illustration
of correct pairing, a reversed pair, crossed pairs, and
split pairs.
 |
Results Interpretation
In most cases you will expect to see straight through connections.
With simple tools, such as LED display testers, a lamp will
light up indicating a short or open. Advanced tests, such
as reversed or split pairs, are often not available in such
equipment. While these tools are usually adequate, it must
be noted that a passing result does not necessarily guarantee
a correct wiring installation. For example, split pair detection
requires the measurement of NEXT or Impedance, which is
beyond the capability of low-end testers. Split pairs will
cause a high degree of NEXT (typically over 22 dB) which
will severely limit available bandwidth on the installed
cabling.
In the case of Screened Twisted Pair cabling you will need
to verify screen continuity. This is usually only available
on more advanced certification tools.
Wire map is a fundamental test, but it is important to
note that correct wiring does not verify bandwidth performance.
Frequency-dependent tests such as NEXT, attenuation, and
return loss are key to ensuring cabling is capable of supporting
high-speed applications.
Troubleshooting Recommendations
In the case of a wire map failure, a careful examination
of the installation (IDC block or connector) will usually
show that one or more wires have been transposed. Inspect
and re-terminate as necessary.
If conductors are missing, it could be because they are
unnecessary for the intended application. For example, 10BASE-T
and token ring each require only four conductors. Some wiring
designs purposely use one four pair cable to supply two
RJ45 connections each with two pairs. The important issue
is to ensure the installed cabling meets the required design
criteria.
If an open conductor is found, use the length measurement
capability of your cable meter to determine whether the
open is at the near or far end to speed fault isolation
and repair.

